The Promising Study Found that 80% of Patients with Mismatch Repair-Deficient (MMRd) Solid Tumors Treated with Immunotherapy Avoided Surgery
The New England Journal of Medicine published a paper on April 27, 2025, that presents exciting new results from a clinical trial led by Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) gastrointestinal oncologists Andrea Cercek, MD, and Luis Diaz Jr., MD, that demonstrates how immunotherapy alone can help patients with MMRd cancers avoid surgery and preserve their quality of life. The results, presented simultaneously at the 2025 American Association of Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting, showed that 80% of patients with several types of cancer treated with immunotherapy did not require surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy after six months of treatment with immunotherapy alone. Swim Across America awarded grants for the early-stage research and continues to award grants for the ongoing clinical trial.

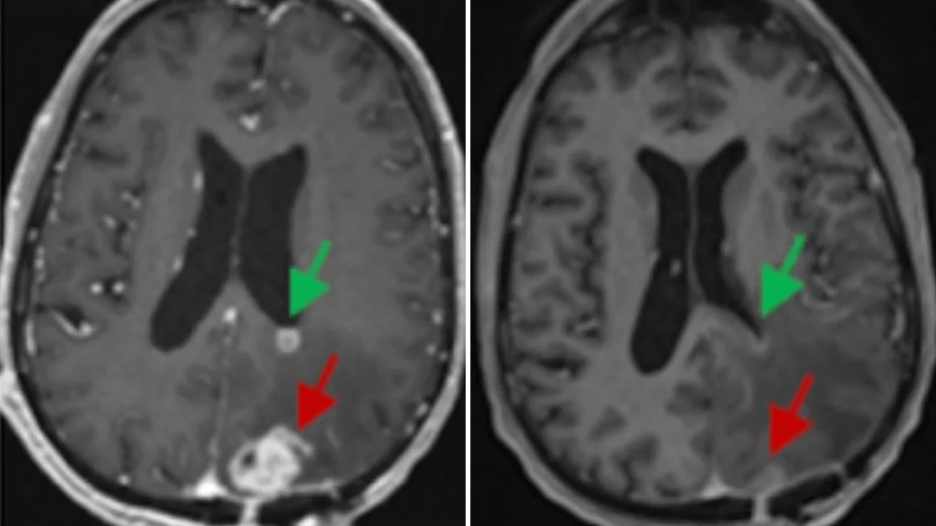
Mismatch repair deficiency (MMRd) in cancer refers to a situation where tumor cells have defective mismatch repair (MMR) proteins, essential for correcting DNA errors during cell replication. This deficiency leads to the accumulation of mutations, including microsatellite instability (MSI), making tumors more prone to be recognized by the immune system. MMRd status is a significant factor in cancer treatment, particularly for immunotherapy, as it can predict response to immune checkpoint inhibitors.
The standard of care for many cancers that have this specific MMRd genetic mutation has been surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Still, the patients who responded positively to this clinical trial did not require surgery to remove an organ and did not experience chemotherapy or radiation, which improved their quality of life. This trial is the first time that immunotherapy has been shown to replace surgery for a variety of solid tumors.
“This study shows that immunotherapy can replace surgery, radiation and chemotherapy for mismatch repair-deficient solid tumors, which could help patients preserve their organs and avoid the harsh side effects of chemo and radiation,” said Andrea Cercek, M.D., gastrointestinal oncologist and co-director of the Center for Young Onset Colorectal and Gastrointestinal Cancer at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. “Preserving a patient’s quality of life, while also successfully achieving positive results in eliminating their cancer, is the best possible outcome. They can return to their daily routines and maintain their independence.”

This phase 2 trial is an extension of a groundbreaking study, also funded in part by Swim Across America, in which all rectal cancer patients treated with the immunotherapy dostarlimab experienced a complete clinical response, meaning their tumors disappeared. This was the first time ever that a clinical trial had a 100% positive response rate.
The updated trial included 103 patients with stage 1-3 cancer; 49 with rectal cancer; and 54 with non-rectal cancers, including gastroesophageal, hepatobiliary, colon, genitourinary, and gynecologic. Drs. Cercek and Diaz noted that the 80% response rate in this expanded clinical trial is very exciting for these types of cancer.
“Grants provided by Swim Across America were critical to our initial study and advancing this trial to phase 2,” said Luis Diaz, M.D., gastrointestinal oncologist and Head of the Division of Solid Tumor Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
Founded in 1987, Swim Across America has raised more than $100 million to fight cancer. In its 38 years of making waves, thousands of volunteers and Olympians have swum the circumference of the earth three times uniting a movement to fight cancer that has created a groundswell of support spanning all generations. Today, more than 24 communities across the U.S. hold charity swims each year, which support innovative cancer research, detection, and patient programs.

Swim Across America’s funding of clinical trials on a national level has helped contribute to four FDA-approved life-saving immunotherapy cancer treatments: Yervoy, Opdivo, Tecentriq, and Keytruda. Swim Across America awards grant to more than 60 projects each year and there are ten named Swim Across America Labs at major institutions.
In addition to Swim Across America grants, this trial received funding from the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, Haystack Oncology, and Stand Up To Cancer. MSK also acknowledges support from GSK, whose PD-1 blockade Jemperli (dostarlimab), represents a promising advancement in the treatment of patients.
For more information and to inquire about eligibility for this clinical trial, talk to your oncologist or call MSK at 646-888-4189. You may also reach to info@swimacrossamerica.org and we will help guide you.